d. Run PyTorch Data Parallel training on ParallelCluster
In this step you will use the PyTorch DistributedDataParallel API to train a Natural Language Understanding model using the Fairseq framework. You will create a SLURM batch script to run the data parallel job across multiple GPU nodes and configure the PyTorch API to distribute tasks between the GPUs in each node.
Create distributed training job scripts
Create a fairseq-train script in the /lustre shared folder with the following commands:
cd /lustre
cat > train.sh << EOF
#!/bin/bash
# set up the Data and checkpoint locations
DATABIN=/lustre/data/wikitext-103
OUTDIR=/lustre/data/out && mkdir -p \$OUTDIR
SAVEDIR=/lustre/checkpoints
# set up environment variables for Torch DistributedDataParallel
WORLD_SIZE_JOB=\$SLURM_NTASKS
RANK_NODE=\$SLURM_NODEID
PROC_PER_NODE=8
MASTER_ADDR_JOB=\$SLURM_SUBMIT_HOST
MASTER_PORT_JOB="12234"
DDP_BACKEND=c10d
# setup NCCL to use EFA
export FI_PROVIDER=efa
export FI_EFA_TX_MIN_CREDITS=64
export NCCL_DEBUG=INFO
export NCCL_TREE_THRESHOLD=0
export NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME=eth0
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$HOME/nccl/build/lib:/usr/local/cuda/lib64:/opt/amazon/efa/lib64:/opt/amazon/openmpi/lib64:\$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
# set up fairseq-train additional arguments
BUCKET_CAP_MB=200
TOTAL_UPDATE=500
MAX_SENTENCES=8
UPDATE_FREQ=1
# calling fairseq-train
python -m torch.distributed.launch \
--nproc_per_node=\$PROC_PER_NODE \
--nnodes=\$WORLD_SIZE_JOB \
--node_rank=\$RANK_NODE \
--master_addr=\${MASTER_ADDR_JOB} \
--master_port=\${MASTER_PORT_JOB} \
\$(which fairseq-train) \
\$DATABIN \
--log-format json --log-interval 25 \
--seed 1 \
--fp16 --memory-efficient-fp16 \
--criterion masked_lm \
--optimizer adam \
--lr-scheduler polynomial_decay \
--task masked_lm \
--num-workers 2 \
--max-sentences \$MAX_SENTENCES \
--ddp-backend \$DDP_BACKEND \
--bucket-cap-mb \$BUCKET_CAP_MB \
--fast-stat-sync \
--arch roberta_large \
--max-epoch 2 \
--max-update \$TOTAL_UPDATE \
--clip-norm 1.0 \
--update-freq \$UPDATE_FREQ \
--lr 0.0006 \
--save-dir \$SAVEDIR \
--sample-break-mode complete \
--tokens-per-sample 512 \
--adam-betas '(0.9, 0.98)' --adam-eps 1e-06 \
--warmup-updates 24000 \
--total-num-update \$TOTAL_UPDATE \
--dropout 0.1 \
--attention-dropout 0.1 \
--weight-decay 0.01 | tee \$OUTDIR/train.\$RANK.\$WORLD_SIZE.log
EOF
chmod +x train.sh
The script starts by setting up paths for the training data, output and checkpointing. All paths reference /lustre and are visible by all compute nodes. Next, the script sets environment variables for the PyTorch DistributedDataParalle API based on the SLURM environment. It also sets the required environment variables for NCCL to work with AWS EFA. The last section contains the command python -m torch.distributed.launch, which launches the training, based on the environment variables previously set. For more information on the DistributedDataParalle API, refer to the documentation here.
Create the SLURM batch script with the following commands:
cd /lustre
cat > job.slurm << EOF
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --wait-all-nodes=1
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:8
#SBATCH --nodes=2
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=5
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1
#SBATCH --exclusive
#SBATCH -o out_%j.out
srun /lustre/train.sh
EOF
This script requests 2 nodes with the argument --nodes=2, same as the maximum number of nodes defined on the cluster configuration file. The argument --gres=gpu:8 requests resources with 8 GPUs, the amount available in each compute instance. With the train.sh and job.slurm scripts, you are ready to execute the multi-node, multi-GPU distributed training job.
Run the distributed data parallel training job
Use the sbatch job.slurm command to launch replicas of the train.sh script across the different nodes:
cd /lustre
sbatch job.slurm
The above commands add a SLURM job to the queue and logs its output to the out_<job_id>.out file. Check the status of the job with squeue -ls and sinfo -ls. If there are less than the requested 2 nodes, ParallelCluster will spin up new instances. This process takes a few minutes.
Once the job starts, you can check the progress by tailing the output file with the following command: tail -f out_<job_id>.out.
As training starts, you will see an output such as the following:
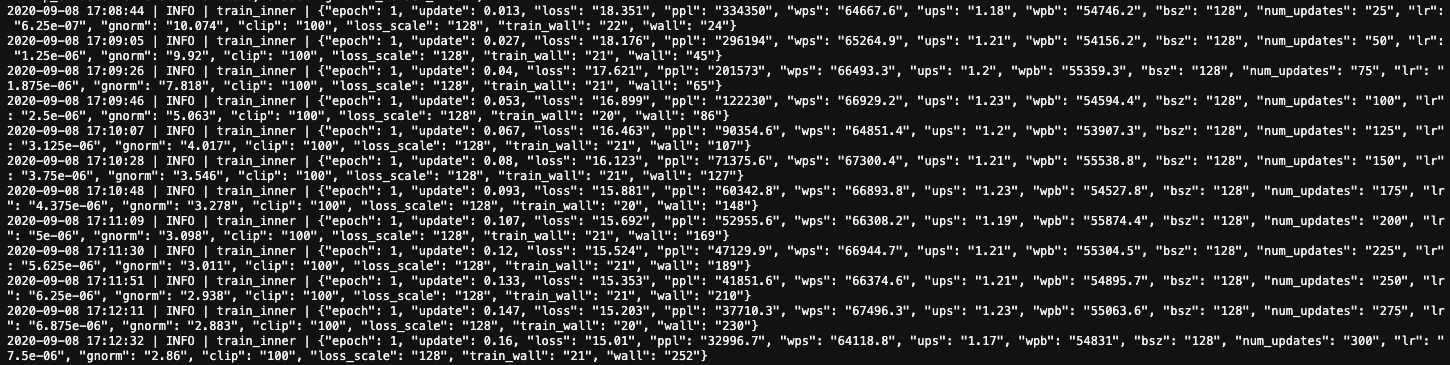
The model is training at approximately 66,000 words per second (wps) on batch size 128, with around 55,000 words per batch (wpb). In this configuration training one epoch takes approximately 9 minutes to complete. At the end of the epoch a model checkpoint file will be created in /lustre/checkpoints and can be used to continue training and further fine tuning.
Fairseq saves the model state at certain points during training in the /checkpoints directory. If you wish to persist the model checkpoints for later use, copy them to the S3 bucket with the following command - make sure to replace <your-bucket-postfix> with your bucket’s id:
cd /lustre
aws s3 cp checkpoints s3://mlbucket-<your-bucket-postfix>/checkpoints --recursive
Next, cleanup!